Greater Short-Horned Lizard Ejects Blood From Eyes When It Feels Threatened
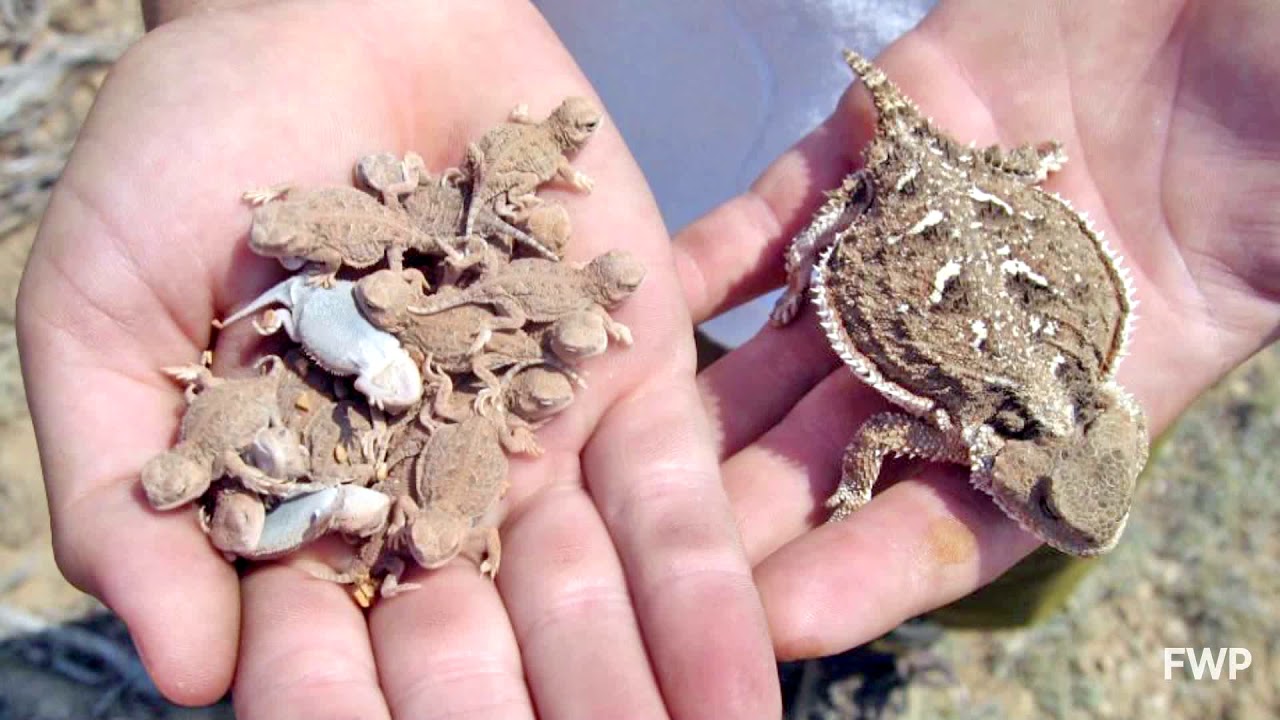
Greater short-horned lizard - The short-horned lizard is frequently alluded to as a "horned toad" or "horny toad" on the grounds that its squat, leveled shape and short, gruff nose give it a toad-ish look.
Author:Xander OddityReviewer:Dr. Felix ChaosphereMay 18, 202245 Shares904 Views

Greater short-horned lizard- The short-horned lizard is frequently alluded to as a "horned toad" or "horny toad" on the grounds that its squat, leveled shape and short, gruff nose give it a toad-ish look.
There are more than twelve perceived horned lizardspecies found in the deserts and semi-bone-dry conditions of North and Central America, from southern Canada to Guatemala.
North American desert horned lizards have a wide scope of hunters inside their living space.
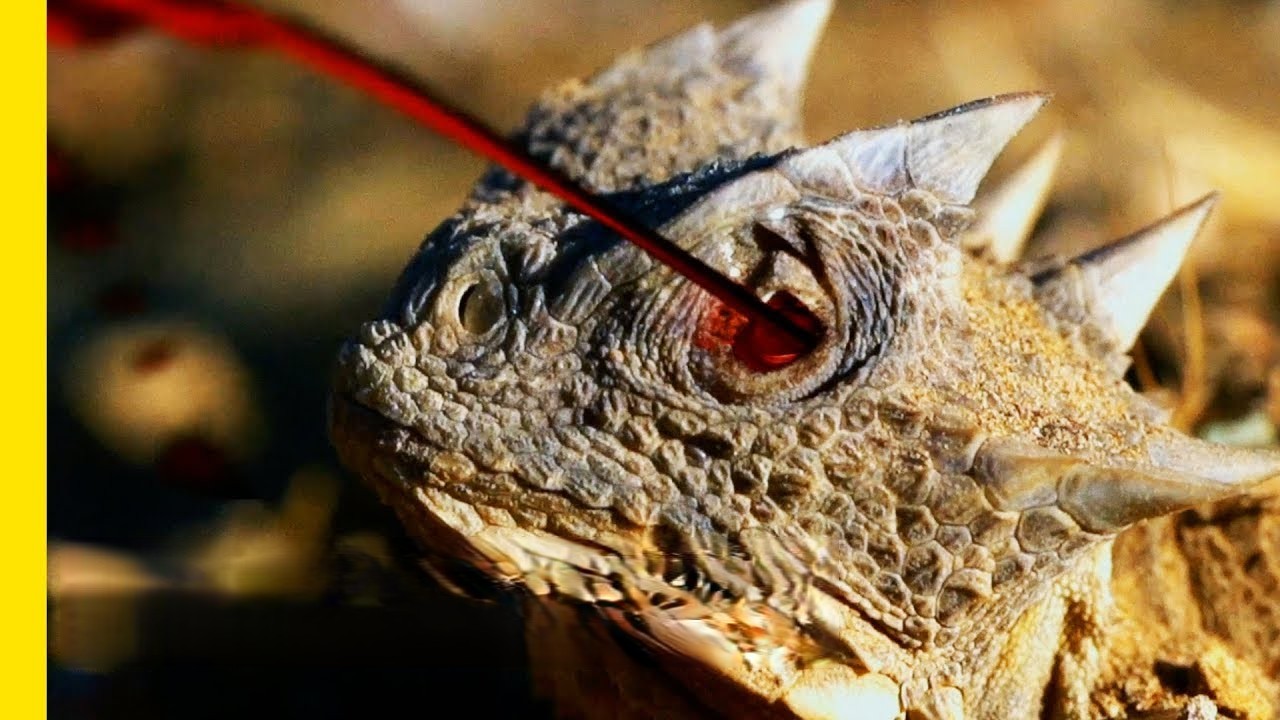
One surprising safeguard component of greater short-horned lizard includes the flooding of their visual sinuses, tissues found beneath their eye, with blood.
At the point when horned lizards feel compromised by a hunter, their last protection reaction is to shoot blood from these overflowed sinuses and out their eye attachments.
Accordingly, the hunter is frequently terrified and escapes.
The lizard additionally utilizes this component to eliminate unfamiliar particles from the outer layer of its eyes.
Attributes And Diet
Species are recognizable by the considerable crown of horns decorating their head and the various spines across their back.
Their shading can be yellowish, dark, or rosy brown contingent upon the climate they occupy, and, joined with their shape, bears the cost of their significant cover on a superficial level.
They feed principally on insects, hanging tight for one to accidentally creep by prior to snapping it in and gulping down it.
They are additionally known to eat grasshoppers, scarabs, and insects.
Defensive Adaptations
Regardless of their spiky highlights, short-horned lizards are gone after by various animals, including falcons, roadrunners, snakes, reptiles, canines, wolves, and coyotes. Thus, past their regular disguise, they have adjusted a couple of momentous abilities.
Why Does The Short Horned Lizard Squirt Blood?
To avoid hungry hunters, short-horned lizards are equipped for swelling their bodies up to two times their size, looking like a sharp inflatable.
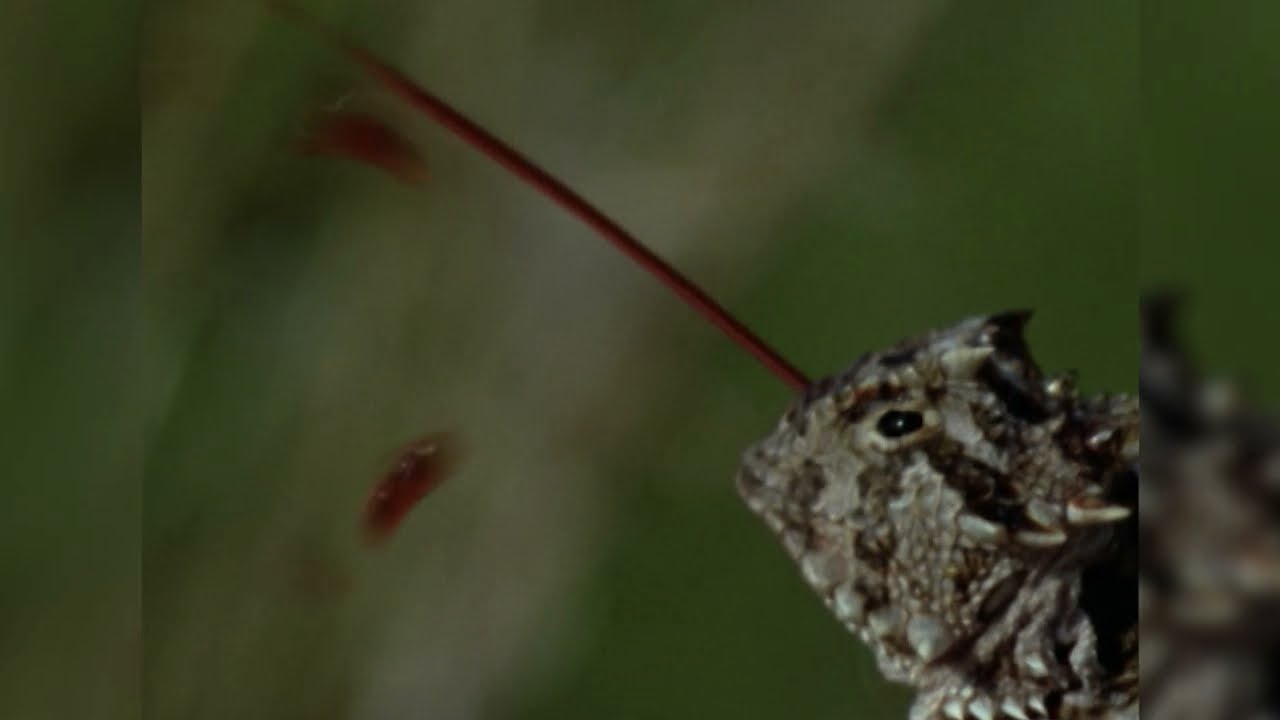
Furthermore, on the off chance that this demonstrates lacking, a few animal varieties utilize one of the animals of the world collectively's most unusual protective instruments: they shoot blood from their eyes.
The inauspicious spurting blood radiates from conduits toward the sides of their eyes and can travel a distance of up to three feet.
It's intended to confound would-be hunters, yet additionally contains a substance that is poisonous to canines, wolves, and coyotes.
The Mechanism
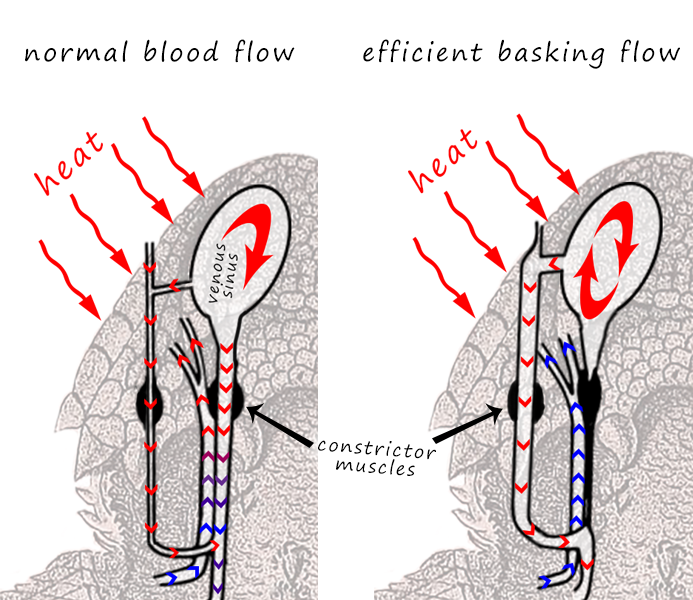
The horned lizard has two constrictor muscles that line the significant veins around its eye.
At the point when these muscles contract, they slice off the bloodstream back to the heart, while it keeps on streaming into the head.
This floods the visual sinuses with blood, building tension, and making them swell. By additional getting these muscles in a quick way, the tension increments much more, in the long run breaking the meager sinus films.
The outcome is a fly stream of blood that can shoot up to four feet from the eye attachment, a cycle known as auto-discharging.
Incredibly, this interaction can be rehashed a few times inside a brief period if important, however, the instrument for this fast recuperation isn't totally perceived.
The lizard utilizes a similar instrument to eliminate particles from its eye, without breaking the sinus layers totally.
At the point when soil, soil, or different particles enter the eye, the lizard controls the tension unequivocally, permitting the sinuses to expand, yet not discharge.
It then clears a flimsy, straightforward third eyelid across the outer layer of the eye.
This membranous eyelid folds back to the front corner of the eye, leaving the garbage at the back corner.
The horned lizard then utilizes the swelling visual sinuses to draw the garbage away from the back of the eye and onto the eyelid.
When the lizard floods its sinuses with blood, as portrayed over, the skin encompassing the eyelids grows, disjoining the garbage where it tumbles off or is generally handily eliminated.
A Reddit user commented on the greater short-horned lizard postthat the blood contains a compound that is harmful to canines, wolves, and coyotes.
Their blood contains formic acid that is especially destructive to individuals from the canine family and causes a troublesome response that deters further crunching.
Dangers To Survival
Over ongoing many years, short-horn lizard populaces have been in decline all throughout their reach.
Obliteration of their local territory, endeavors to destroy subterranean insects — their staple food — and the pet exchange have all added to this.
People Also Ask
Do Horned Lizards Shoot Blood At Humans?
If all else fails, horned lizards might utilize one last guard component that is especially compelling against hunters like catamounts, wolves, and coyotes. They shoot blood from their eye attachments! This typically scares hunters enough to make them escape. Luckily for people, horned lizards seldom shoot blood at individuals.
Why Do Horned Toads Squirt Blood?
The horny toad utilizes a few protection components, with blood-spurting utilized exclusively if all else fails. Their shading assists them with mixing into their environmental elements and ideally try not to be seen by hunters.
Conclusion
The mechanism of greater short-horned lizard utilized in fluid administrations, for example, siphons or channels need standard upkeep to keep them clean. Frequently, this requires closing plants and cycles down to perform such upkeep.
Concentrating on this lizard's one-of-a-kind instrument could give creative ways of cleaning gear while it keeps on working, expanding general productivity.

Xander Oddity
Author
Xander Oddity, an eccentric and intrepid news reporter, is a master of unearthing the strange and bizarre. With an insatiable curiosity for the unconventional, Xander ventures into the depths of the unknown, fearlessly pursuing stories that defy conventional explanation. Armed with a vast reservoir of knowledge and experience in the realm of conspiracies, Xander is a seasoned investigator of the extraordinary.
Throughout his illustrious career, Xander has built a reputation for delving into the shadows of secrecy and unraveling the enigmatic. With an unyielding determination and an unwavering belief in the power of the bizarre, Xander strives to shed light on the unexplained and challenge the boundaries of conventional wisdom. In his pursuit of the truth, Xander continues to inspire others to question the world around them and embrace the unexpected.

Dr. Felix Chaosphere
Reviewer
Dr. Felix Chaosphere, a renowned and eccentric psychiatrist, is a master of unraveling the complexities of the human mind. With his wild and untamed hair, he embodies the essence of a brilliant but unconventional thinker. As a sexologist, he fearlessly delves into the depths of human desire and intimacy, unearthing hidden truths and challenging societal norms.
Beyond his professional expertise, Dr. Chaosphere is also a celebrated author, renowned for his provocative and thought-provoking literary works. His written words mirror the enigmatic nature of his persona, inviting readers to explore the labyrinthine corridors of the human psyche.
With his indomitable spirit and insatiable curiosity, Dr. Chaosphere continues to push boundaries, challenging society's preconceived notions and inspiring others to embrace their own inner tumult.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles